Installing PVE#
Directly download the ISO image from the official website, and then follow the prompts to install it.
During the installation, remember to record the information in the Summary and Install Successful sections, as you may need it later.
After the first installation, if you want to access SSH, WebGUI, etc., you need to first connect to the management network port specified during installation (here it is enp6s0), and then set the computer’s network card to an IP address in the same subnet as the PVE host but different from it. If you still can’t access it, you can try disabling other network connections (such as WiFi).
Setting up PVE#
Setting up Hardware Passthrough#
Since I want to pass through some network cards to OPNsense, I need to modify the settings to enable hardware passthrough in PVE.
In the WebGUI, log in to the Shell at the node and modify the grub file /etc/default/grub: change the value of the GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT=quite line to quite intel_iommu=on (for AMD, it’s amd_iommu=on). After saving, use update-grub to update.
Modify the /etc/modules file and add the following content:
vfio
vfio_iommu_type1
vfio_pci
vfio_virqfd
After saving, restart the machine.
Run the following command to list all IOMMU groups:
#!/bin/bash
shopt -s nullglob
for g in `find /sys/kernel/iommu_groups/* -maxdepth 0 -type d | sort -V`; do
echo "IOMMU Group ${g##*/}:"
for d in $g/devices/*; do
echo -e "\t$(lspci -nns ${d##*/})"
done;
done;
Hardware Passthrough Troubleshooting#
Since I have a wireless network card that I want to pass through to the OPNsense virtual machine, and if I set up passthrough directly, qemu will report an error: failed to add PCI capability 0x11[0x70]@0x90: table & pba overlap, or they don't fit in BARs, or don't align.
Here, you need to do one more step: modify PVE’s /etc/pve/qemu-server/[VM ID].conf and add a line to the file:
# Here the wireless network card is assigned to hostpci4 in the virtual machine, modify as needed
args: -set device.hostpci4.x-msix-relocation=bar2
For more information, you can refer to: Failed to PCI passthrough SSD with SMI SM2262 controller. - Kernel.org Bugzilla, PCIe Passthrough of Atheros AR9280 - Promox Forums
Installing and Setting up OPNsense#
Installing OPNsense#
Enter the PVE WebGUI and upload the OPNsense ISO installation package.
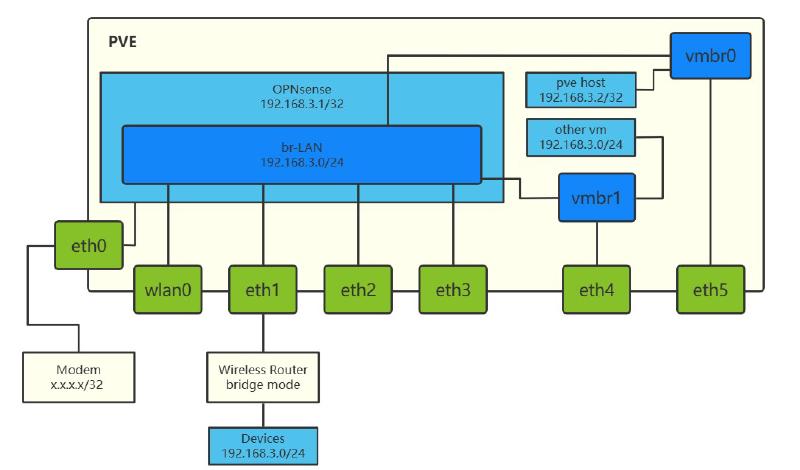
Create a new network card bridge at the PVE node, select a network card different from the management network card, and only fill in the Bridge Ports field. The name here is vmbr1.
Create a new virtual machine, set the parameters (remember to enable the AES function in the CPU settings), add the network device vmbr1, and in Hardware, add a PCI device, adding only enp1s0 for now.
Start the virtual machine, and you will first enter live mode (demo mode). Before entering demo mode, you will configure network information. It is recommended to manually configure the WAN and LAN ports here. Here, the enp1s0 port connected to the optical modem is set as the WAN, and the bridged network card vtnet0 is set as the LAN port.
After successfully entering demo mode, log in with the username installer and password opnsense to enter installation mode, complete the subsequent installation, and set the administrator password.
After the installation is complete, restart the virtual machine and remove the installation media.
Initial Setup#
Connect the computer to the network port corresponding to enp5s0, and change the computer’s manual address back to DHCP automatic acquisition. Log in to the OPNsense WebGUI with the default address 192.168.1.1 and complete the initial setup wizard. In the setup wizard, you can change the LAN port address to avoid conflicts with the optical modem’s 192.168.1.1 (it is recommended to be in the same subnet as PVE, the reason will be mentioned later). After applying the settings, wait for a while (a relatively long time), and then access the WebGUI interface with the new address.
Configuring Multiple Network Ports#
Reference: How to set up a LAN Bridge - OPNsense Docs
Plug the network cable back into the network port corresponding to enp6s0, reset the computer’s address, shut down the OPNsense virtual machine, and add the enp2s0, enp3s0, and enp4s0 network cards. Restart the virtual machine.
Return to the OPNsense WebGUI as described above. In Interfaces ‣ Assignments, create all the newly added ports and save the settings. Then, in Interfaces ‣ [each newly added network port], enable all the newly added network ports and apply the changes.
In Interfaces ‣ Other Types ‣ Bridge, create a new br-LAN bridge, and then add all other network ports except the one originally added as the LAN port. Go back to Interface ‣ Assignments, change the LAN port (the one with “lan” after the identifier name) to br-LAN, save and apply. At this point, the connection to OPNsense will be disconnected. You can reconnect by connecting the computer to other LAN ports.
After a successful connection, follow the same procedure to add the original network port to br-LAN, save and test whether you can access the OPNsense WebGUI.
In System ‣ Settings ‣ Tunables, change net.link.bridge.pfil_member to 0 and net.link.bridge.pfil_bridge to 1 to modify the firewall behavior.
Configuring PVE to be Accessible from the Intranet#
I haven’t found any other good way.
The current solution is to set the IP range of OPNsense and PVE to the same subnet (e.g., 192.168.3.x/24), and then add the bridge vmbr0 where the PVE management port is located to the OPNsense VM. In OPNsense, enable this network port and add it to br-LAN. Because the OPNsense DHCP server allocates IP addresses starting from 192.168.3.10/24 by default, PVE is given the static IP address 192.168.3.2/24. This way, you can access the PVE WebGUI from the intranet by visiting https://192.168.3.2:8006.
When OPNsense is down, you can connect to the management port and manually configure the IP address in the same subnet for emergency connection.
Configuring AP#
In Interfaces ‣ Wireless, create a clone of the wireless network card, then go to Interfaces ‣ Assignments to add the wireless network card’s port, save and apply.
After successfully adding the network port, enable it in the corresponding network port settings and set the following:
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Standard | 802.11na |
| Mode | Access Point |
| SSID | WiFi Name |
| Allow intra-BSS communication | True |
| WPA | Enable WPA |
| WPA Pre-Shared Key/EAP Password | WiFi Password |
| WPA Mode | WPA2 |
| WPA Key Management Mode | Pre-Shared Keys |
| WPA Pairwise | AES |
Finally, add the wireless network port to br-LAN to complete the setup.
Configuring Transparent Proxy#
Reference: A method for using transparent proxy for scientific Internet access in OPNsense - OPNsense Forum
Installing Clash#
First, enable the SSH connection method for OPNsense: in System ‣ Settings ‣ Administration, Enable Secure Shell, and allow root login and password login, save and apply the settings.
Log in to OPNsense via SSH, create a new folder /usr/local/clash, and put the FreeBSD version of the binary file, configuration file, and yacd panel file into it.
Use pw user add clash -c "Clash" -s /usr/sbin/nologin to create a non-login account, and grant file ownership to the newly created user clash:clash. After completion, run it once on the spot for initialization.
Creating a System Service#
Create a new file /usr/local/etc/rc.d/clash
#!/bin/sh
# $FreeBSD$
# PROVIDE: clash
# REQUIRE: LOGIN cleanvar
# KEYWORD: shutdown
# Add the following lines to /etc/rc.conf to enable clash:
# clash_enable (bool): Set to "NO" by default.
# Set to "YES" to enable clash.
# clash_config (path): Clash config dir.
# Defaults to "/usr/local/etc/clash"
. /etc/rc.subr
name="clash"
rcvar=clash_enable
load_rc_config $name
: ${clash_enable:="NO"}
: ${clash_config="/usr/local/clash"}
command="/usr/local/clash/clash"
#pidfile="/var/run/clash.pid"
required_files="${clash_config}"
clash_group="clash"
clash_user="clash"
command_args="-d $clash_config"
run_rc_command "$1"
and grant execution permission chmod +x /usr/local/etc/rc.d/clash
Create a new file /usr/local/opnsense/service/conf/actions.d/actions_clash.conf
[start]
command:/usr/local/etc/rc.d/clash onestart
type:script
message:starting clash
[stop]
command:/usr/local/etc/rc.d/clash stop
type:script
message:stoping clash
[status]
command:/usr/local/etc/rc.d/clash statusexit 0
type:script_output
message:get clash status
[restart]
command:/usr/local/etc/rc.d/clash onerestart
type:script
message:restarting clash
and enable service configd restart
Finally, go to Services ‣ Monit ‣ Settings to enable Monit, and add two in Service Test Settings:
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | Clash |
| Condition | failed host 127.0.0.1 port 7890 type tcp |
| Action | Restart |
Second, to avoid a restart loop
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | RestartLimit4 |
| Condition | 5 restarts within 5 cycles |
| Action | Unmonitor |
Add in Service Settings:
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | Clash |
| Match | clash |
| Start | /usr/local/sbin/configctl clash start |
| Stop | /usr/local/sbin/configctl clash stop |
| Tests | Clash,RestartLimit4 |
Finally, wait for a while and check if it is running in Monit ‣ Status.
Configuring Transparent Proxy#

Using WireGuard for Transparent Proxying in OPNsense (Advanced)
In Services ‣ Web Proxy ‣ Administration’s General Proxy Settings, enable the proxy. In Forward Proxy, enable Enable Transparent HTTP proxy, Enable SSL inspection, Log SNI information only, and click on the “Add a new firewall rule” text in the prompt for each column (i) (Note! Remember to apply after adding the NAT item!).
Then go to System ‣ Trust ‣ Authorities to create a new certificate with the following settings:
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Descriptive name | OPNsense-SSL |
| Method | Create an internal Certificate Authority |
| Key length (bits) | 2048 |
| Digest Algorithm | SHA256 |
| Lifetime (days) | 356 |
| Country Code | NL (Netherlands) |
| State or Province | Zuid Holland |
| City | Middelharnis |
| Organization | OPNsense |
| Email Address | spam (at) opnsense.org |
| Common Name | opnsense-ssl-ca |
After creating the certificate, go back to Services ‣ Web Proxy ‣ Administration’s Forward Proxy and select the newly created certificate for CA to use.
After completing the settings, do not set the upstream proxy yet. Visit any web page, and then check if there are access logs in Web Proxy ‣ Access Log. (A reminder: if you find no response for a long time, it may be that the NAT has created an item but has not been applied).
Finally, set the upstream proxy. In Web Proxy ‣ General Proxy Settings ‣ Parent Proxy Settings, enable it and set it to 127.0.0.1:7890.
A script to automatically update the core and configuration files#
I took a little shortcut and asked ChatGPT (3.5) to help me write this script update.sh. You just need to place this script anywhere and configure it, and you can easily and quickly update the core and configuration files.
Here are the places that need to be modified in this script:
current_directoryis the folder where the update needs to be performed. If you follow the previous steps, this part does not need to be changed;download_config_urlis the download address of the configuration file, update it as needed;update_core_proxyandupdate_config_proxyare the http/socks5 proxies used when updating the kernel and configuration, respectively. If they are empty, they will not be used;download_ui_urlis the link to downloadui.zip. The link in the file is the download link for the MetaCubeX/metacubexd panel. After downloading, you need to unzipui.zipto the corresponding directory yourself. It follows the setting ofupdate_core_proxy;- The repository information part is the repository owner
repo_ownerand the repository namerepo_name. The one provided in the file is the Stable version of Clash.Meta; - In
repo_filename,<version>will be replaced with the latest version obtained in real time.
#!/bin/sh
# Set the variable for the current working directory
current_directory="/usr/local/clash"
# Define the link to download config.yaml
download_config_url="http://openmediavault:25500/getprofile?name=profiles/default.ini&token=xxx"
# Define the link to download ui.zip
download_ui_url="https://github.com/MetaCubeX/metacubexd/archive/refs/heads/gh-pages.zip"
# Define the Clash core GitHub repository information
repo_owner="MetaCubeX"
repo_name="Clash.Meta"
repo_filename="clash.meta-freebsd-amd64-<version>.gz"
# Add proxy variables
update_core_proxy="socks5://opnsense:7891"
update_config_proxy=""
# Define the current update command to be executed
current_command=$1
# Help document function
print_help() {
echo "Usage: $0 [config|core|ui|stop|help]"
echo "Commands:"
echo " config Update the config.yaml file"
echo " core Download the latest clash executable and replace it"
echo " ui Download the latest ui.zip file"
echo " stop Stop the clash process"
echo " help Display the help document"
}
# Backup and replace file function
backup_file() {
if [ -f "$1" ]; then
mv -f "$1" "$1.bak"
fi
}
# Stop the process and set permissions
stop_and_cleanup() {
echo "Stopping the Clash process:"
chown -R clash:clash $current_directory
/usr/local/sbin/configctl clash stop
}
# Define the signal handler function
interrupt_handler() {
echo "Download was interrupted."
# Choose whether to replace the file based on the currently executing command
if [ "$current_command" = "core" ]; then
# If downloading the core, restore the backed-up clash (if it exists)
if [ -f "$current_directory/clash.bak" ]; then
cp -f "$current_directory/clash.bak" "$current_directory/clash"
echo "Restored the backed-up Clash."
fi
elif [ "$current_command" = "config" ]; then
# If downloading the config, restore the backed-up config.yaml.bak (if it exists)
if [ -f "$current_directory/config.yaml.bak" ]; then
cp -f "$current_directory/config.yaml.bak" "$current_directory/config.yaml"
echo "Restored the backed-up config.yaml.bak."
fi
fi
stop_and_cleanup
exit 1
}
# Set the signal handler
trap interrupt_handler SIGINT
# Function to get the download link for the latest version of the clash executable
get_core_latest_version() {
local proxy_option="$1" # Accept the incoming core_proxy as a parameter
# Get the latest release version information
release_url="https://api.github.com/repos/$repo_owner/$repo_name/releases/latest"
latest_release_info=$(curl $proxy_option -s "$release_url")
# Extract the latest version number from the version information
latest_version=$(echo "$latest_release_info" | grep -oE '"tag_name": "[^"]+"' | head -n 1 | cut -d '"' -f 4)
# Return the latest version number
echo "$latest_version"
}
# Handle the config command
if [ "$current_command" = "config" ]; then
# Backup and overwrite config.yaml.bak
backup_file "$current_directory/config.yaml"
# Set the proxy, if any
config_proxy=""
[ -n "$update_config_proxy" ] && config_proxy="-x $update_config_proxy"
# Use curl to download the file and rename it to config.yaml
curl $config_proxy -# -fSL -o "$current_directory/config.yaml" "$download_config_url"
download_result=$? # Save the exit code of the curl command
# Check if the download was successful
if [ $download_result -eq 0 ]; then
echo "config.yaml updated successfully!"
else
echo "Download failed. Please check if the URL is correct or if the network connection is normal."
# If the download fails, restore the backed-up config.yaml.bak (if it exists)
if [ -f "$current_directory/config.yaml.bak" ]; then
cp -f "$current_directory/config.yaml.bak" "$current_directory/config.yaml"
echo "Restored the backed-up config.yaml.bak."
fi
fi
stop_and_cleanup
# Handle the core command
elif [ "$current_command" = "core" ]; then
# Backup and replace the clash file
backup_file "$current_directory/clash"
# Set the proxy, if any
core_proxy=""
[ -n "$update_core_proxy" ] && core_proxy="-x $update_core_proxy"
# Get the download link for the latest version of the clash executable
latest_version=$(get_core_latest_version "$core_proxy")
# Update repo_filename, replacing <version> with the actual version number
repo_filename=$(echo "$repo_filename" | sed "s/<version>/$latest_version/")
# Build the download link
download_core_url="https://github.com/$repo_owner/$repo_name/releases/download/$latest_version/$repo_filename"
echo "Download link: $download_core_url"
# Download the latest clash executable and unzip it
curl $core_proxy -# -fSL "$download_core_url" | gunzip > "$current_directory/clash"
download_result=$? # Save the exit code of the curl command
chmod +x "$current_directory/clash"
# Check if the update was successful
if [ $download_result -eq 0 ]; then
echo "Clash core updated successfully!"
echo "Latest version: $latest_version"
else
echo "Clash update failed."
# If the update fails, restore the backed-up clash (if it exists)
if [ -f "$current_directory/clash" ]; then
cp -f "$current_directory/clash.bak" "$current_directory/clash"
echo "Restored the backed-up clash."
fi
fi
stop_and_cleanup
# Handle the ui command
elif [ "$current_command" = "ui" ]; then
# Backup and overwrite ui.zip.bak
backup_file "$current_directory/ui.zip"
# Set the proxy, if any
ui_proxy=""
[ -n "$update_core_proxy" ] && ui_proxy="-x $update_core_proxy"
# Use curl to download the ui.zip file to the current directory
curl $ui_proxy -# -fSL -o "$current_directory/ui.zip" "$download_ui_url"
download_result=$? # Save the exit code of the curl command
# Check if the download was successful
if [ $download_result -eq 0 ]; then
echo "ui.zip updated successfully! Please unzip it to the specified folder yourself."
else
echo "Failed to download ui.zip. Please check if the URL is correct or if the network connection is normal."
[ -f "$current_directory/ui.zip" ] && rm "$current_directory/ui.zip" # If the download fails and the file exists, delete it
fi
# Handle the stop command
elif [ "$current_command" = "stop" ]; then
stop_and_cleanup
# Handle the help command or unknown commands
else
print_help
fi
(To be honest, when I was collaborating with ChatGPT on this script, everything went very smoothly and comfortably in the early stages when it wasn’t too complicated. But as the requirements became more and more numerous and the code became more and more complex, ChatGPT started to make all kinds of small mistakes, and in the end, I had to complete the final code modification and integration myself. Maybe the model I used was not powerful enough, I’m waiting for someone to let me use a 4.0 model for free (just kidding))
Setting up Website to Bypass Proxy#
Some services are very strange, even if you set them to direct connection in the Clash rules, they still don’t work (I’m talking about you, Xuexi Qiangguo), I guess they have some way to detect transparent proxies. Here, I choose to create a NAT rule to bypass the proxy for that domain.
First, create an entry NoRedirect1 in Firewall ‣ Aliases, select Hosts as the type, and enter the domain name or IP address as the content, save and apply. You can check whether the domain name is successfully resolved to an IP address in Firewall ‣ Diagnostics ‣ Aliases by selecting the corresponding rule set.
Secondly, in Firewall ‣ NAT, create another rule before the two transparent proxy rules:
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| No RDR (NOT) | True |
| Interface | LAN |
| Protocol | TCP/UDP |
| Source | LAN net |
| Source port range | any to any |
| Destination | NoRedirect1 |
| Destination port range | any to any |
Setting up Only Specified Devices to Go Through the Proxy#
Similar to the previous step, create an entry ProxyMAC1 in Firewall ‣ Aliases, select MAC address as the type, and enter the MAC address of the device that needs to go through the proxy (remember to disable the random MAC address function on the device), save and apply.
Then, in the two NAT rules created in the previous steps, change the Source entry from LAN net to ProxyMAC1, and then you can save and apply.
Installing and Setting up Ubuntu Server#
There are no special points to note, just select vmbr1 as the network device when creating a new virtual machine, and you can access the Internet.
Setting up a Router with OpenWRT as a Pure AP Mode#
In LuCI’s Network ‣ Interfaces, delete all WAN ports.
Configure the LAN port:
General Settings:
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Protocol | Static address |
| Device | br-lan |
| IPv4 address | 192.168.3.3/24 |
| IPv4 gateway | 192.168.3.1 |
Advanced Settings:
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Use custom DNS servers | 192.168.3.1 |
| Delegate IPv6 prefixes | False |
Firewall Settings:
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Create / Assign firewall-zone | unspecified |
DHCP Server:
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Ignore interface | True |
Then plug the network cable from the soft router into the LAN port of the wireless router.
Finally, configure the WiFi with the regular settings to complete the setup.

